Here we will learn about Venn diagrams, including what they are, what they represent, their uses and key set notation.
There are also Venn diagram worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
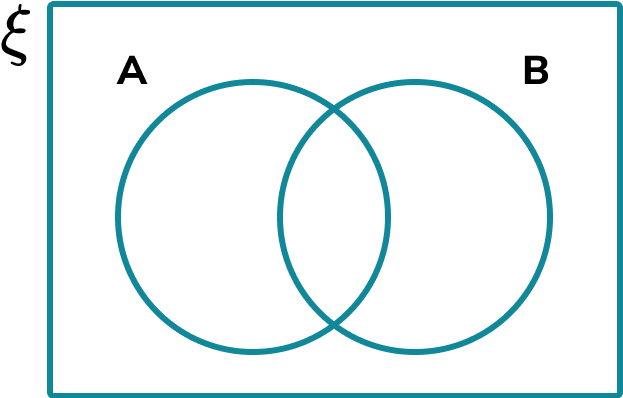
A Venn diagram is a diagrammatic representation of two or more sets.

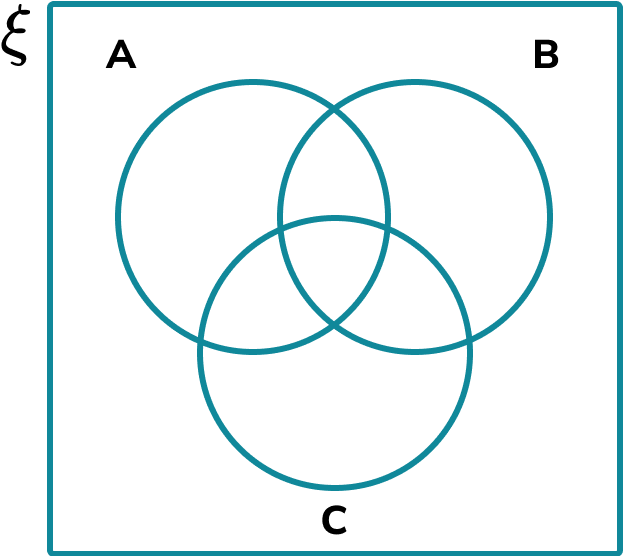
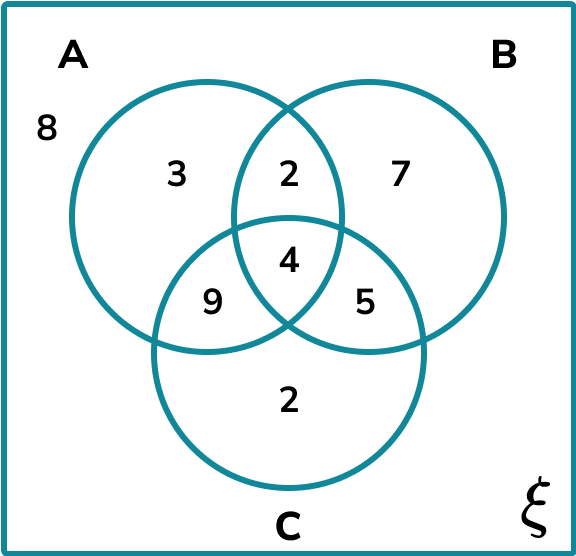
Above are examples of a two set and a three set Venn diagram with the following features:
To analyse data using Venn diagrams, all of the values within each set must be correctly allocated into the correct part of the Venn diagram. The number of sets is usually outlined or logically deduced from the information provided.
To construct a Venn diagram, we draw a region containing two or more overlapping circles (or ellipses), each representing a set, and fill in the relevant information that is either given, or can be logically deduced.
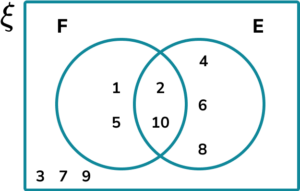
For example, this Venn diagram shows the set of numbers \xi=\ which have been sorted into factors of 10 (F) and even numbers (E).
To describe a subset, we need to understand key symbols and set notation for different sets including the intersection of sets, the union of sets and the absolute complement of sets.
Here are some common examples of set notation and their meaning,
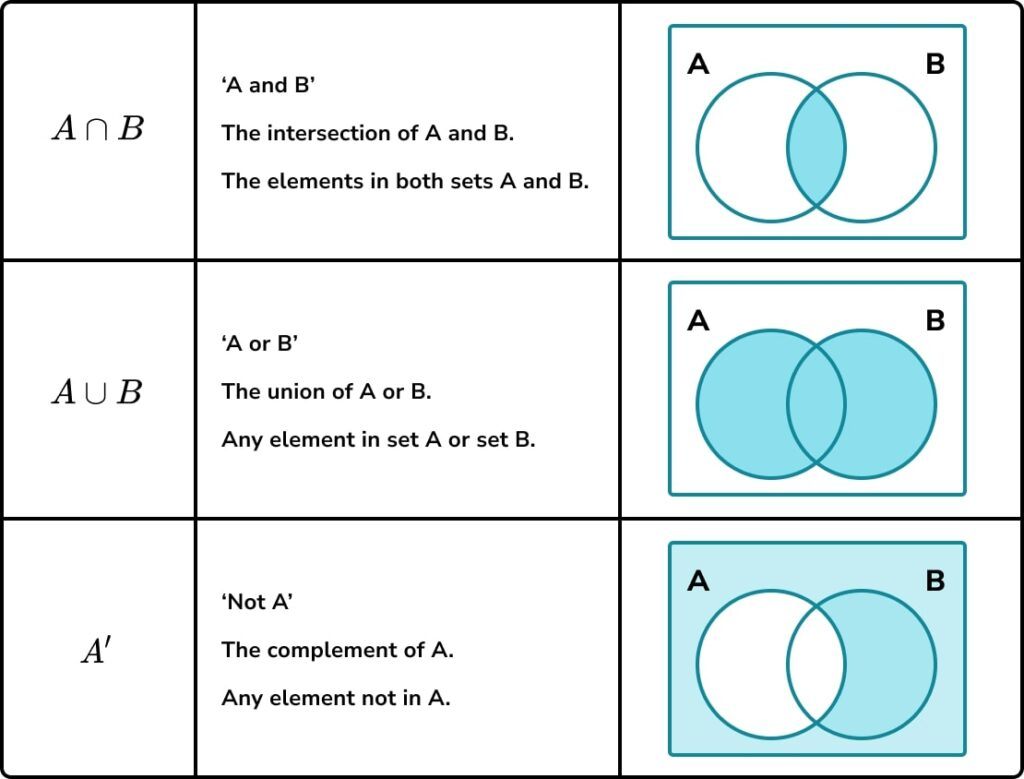
We can use combinations of these, for example
Step-by-step guide: Venn diagram symbols
To calculate the number of items in a subset of a Venn diagram, we need to add together the frequencies of the required subset.
For example, this Venn diagram shows the number of people who own a cat (C) or a dog (D).
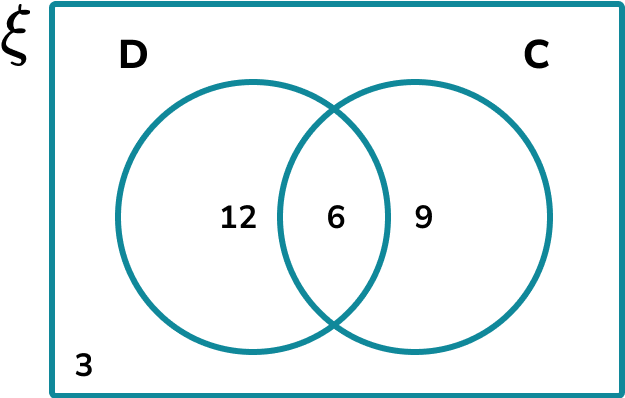
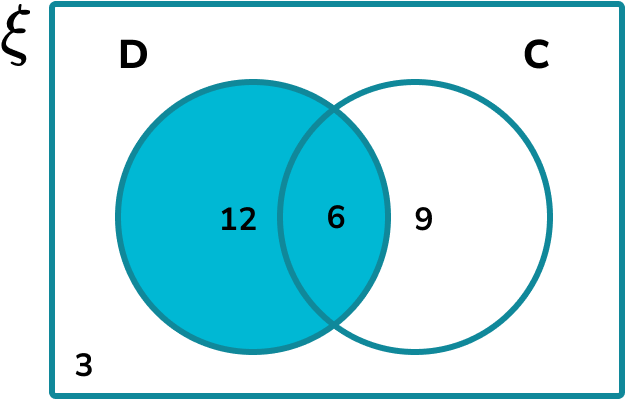
To find the total number of people who own a dog, we need to include everyone in set D.
The number of people who own a dog is 12+6=18 .
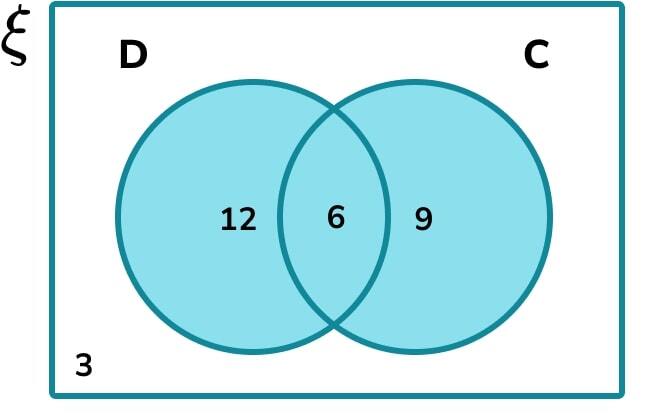
To find the total number of people
who own a dog or a cat, we need
to include everyone in set C or set D.
The number of people who own
a cat or a dog is 12+6+9=27 .
Step-by-step guide: Set notation
To calculate a Venn diagram probability, we need to know each frequency within a subset and the frequency of the larger set which the probability is conditioned on.
For example, this Venn diagram shows the number of people who like Chinese food (C) and Indian food (I).
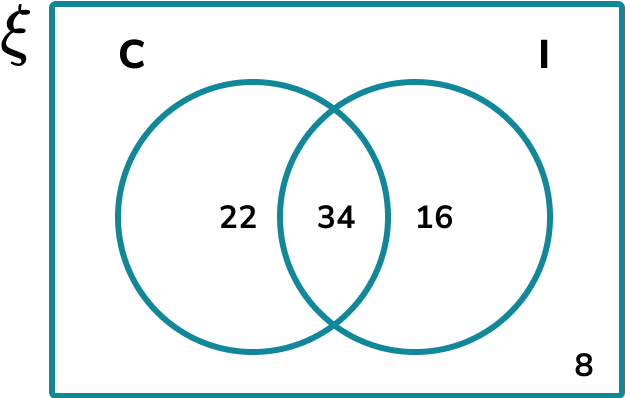
We can find the probability that a person likes Chinese and Indian food.
Here, the probability that a person chosen at random likes Chinese and Indian food, written \text(\text \cap \text), is \frac since 34 people like Chinese and Indian food out of 80 people in total.


Get your free Venn diagram worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.


Get your free Venn diagram worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
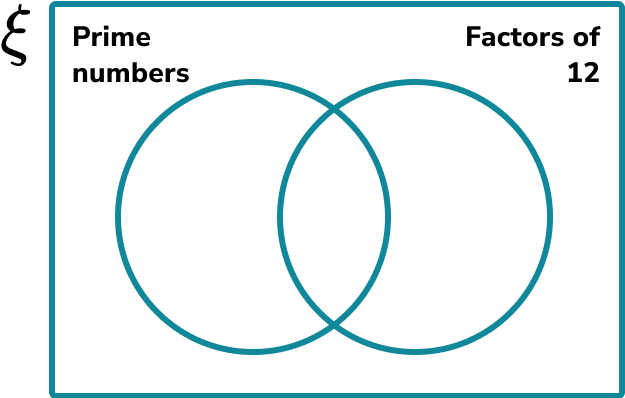
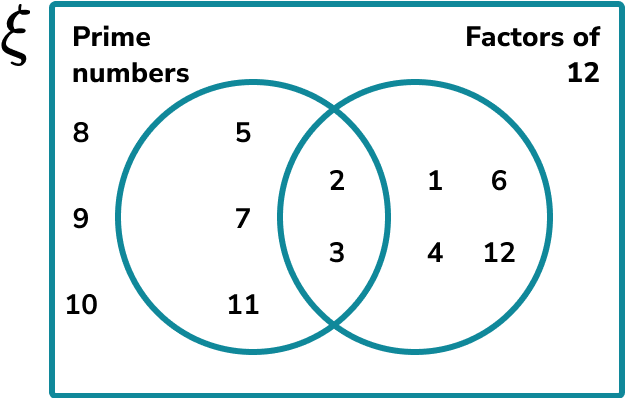
The set \xi = \. Draw a Venn diagram that shows the distribution of the values in the set \xi into the two following sets:

2 Draw the overlapping circles within the universe and label.
The first circle should be labelled with the name of the set Prime Numbers. The second circle should be labelled Factors of 12.
3 Fill in the information for each subset within the Venn diagram.
Place each item in the universal set into the correct part of the Venn diagram.
Top tip: Go through each item in order so you don’t miss any values.
So far we have the following Venn diagram,
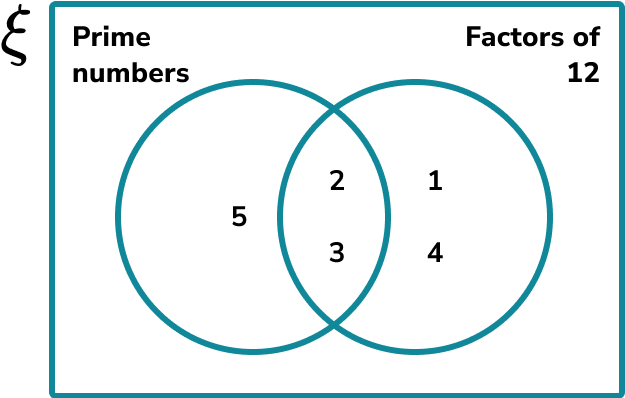
Continuing this process, we get the final solution,
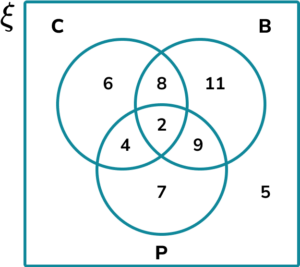
A research group divided 40 construction workers into three groups based on the following criteria,
10\% of the participants satisfy all three criteria.
\frac of the construction workers satisfy at least 2 of the three criteria.
Complete the following three circle Venn diagram to represent the distribution of the participants in the research study.
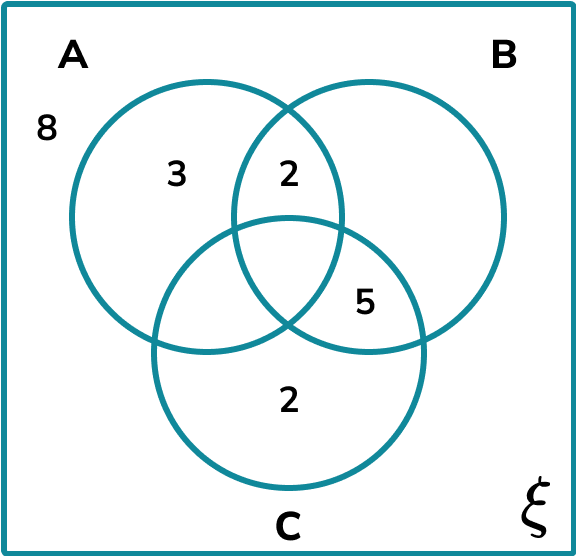
Draw the rectangular universe.
The universal set is already given and so we can move on to the next step.
Draw the overlapping circles within the universe and label.
The three sets have already been given and so we can move on to the next step.
Fill in the information for each subset within the Venn diagram.
As 10\% of participants are within all three sets, the very centre of the Venn diagram where all three sets overlap would contain the value,
(40 \div 100) \times 10=4 .
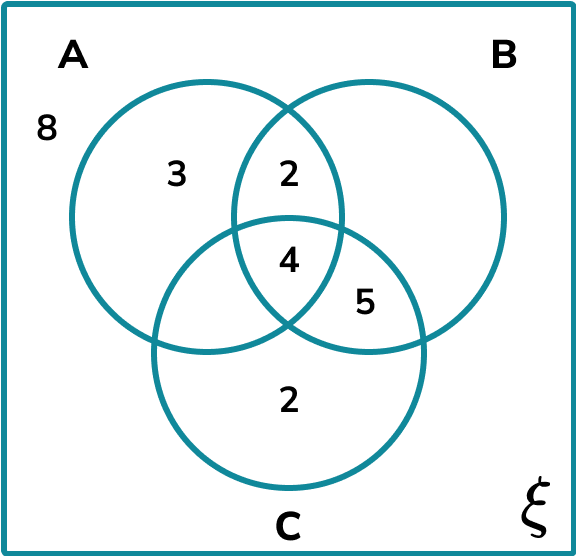
As \frac of the participants are in at least 2 of the three sets, 40\times\frac=20.
The missing value in the intersection between A and C is therefore 20-(2+4+5)=9.
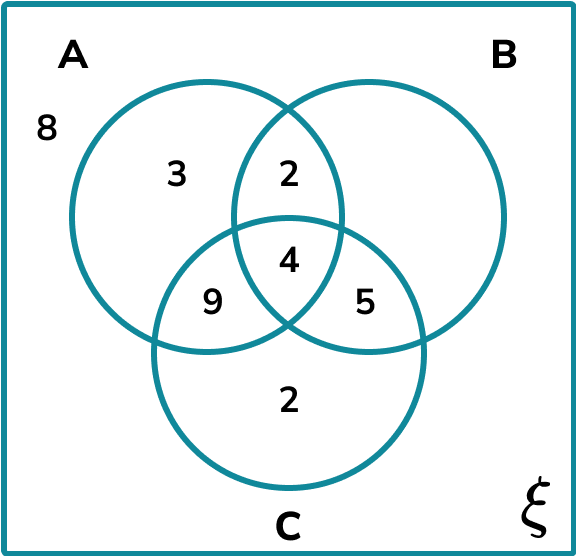
The final missing value for set B is the number of remaining participants. This is equal to
This gives us the completed Venn diagram.
State the name of the subset that is the shaded region in the Venn diagram below,
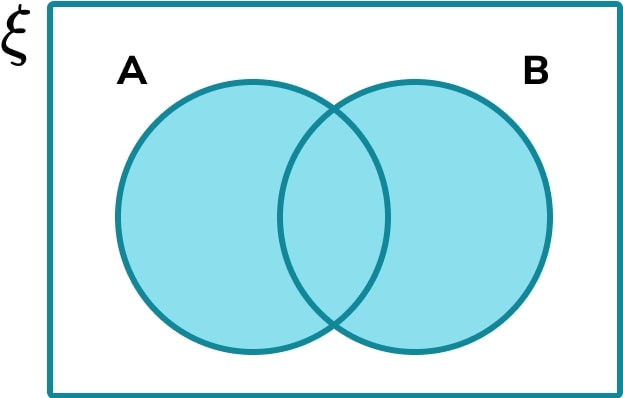
Determine which sets are included in the shaded region.
Every value in set A and every value in set B are included in the shaded region.
Determine which sets are not included in the shaded region.
Every value not in the set A or B is not included in the shaded region.
State the set notation for the shaded region.
As every region within set A or set B is shaded, this is the union of set A and set B, written as A \cup B.
Solution: A \cup B
A meteorologist recorded the daily weather patterns over the month of November.
The two factors that he wants to look at are
Below is a Venn diagram of his results.
Determine the frequency of the set S \cup T’.
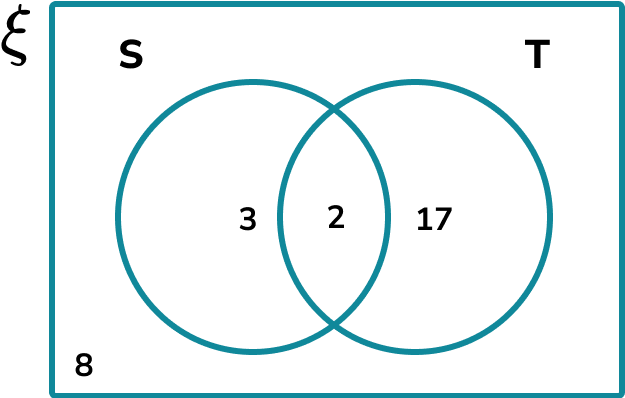
Calculate the frequencies in each subset of the Venn diagram.
The subset S \cup T’ is the union of all of the values in the set S or all of the values not in the set T. This is the following shaded region:
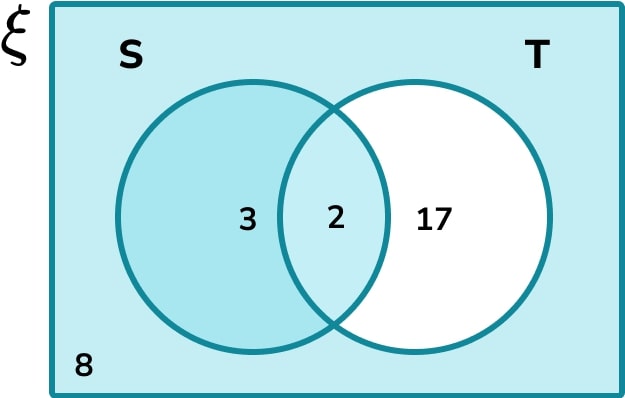
Add all of the frequencies within the two sets.
Do not count any duplicated values twice. We only add each value within the two sets once, to get 8+3+2=13.
Solution: S \cup T’ =13.
40 musicians were asked if they could play the Violin (V) or the Piano (P). The results are shown in the Venn diagram below.
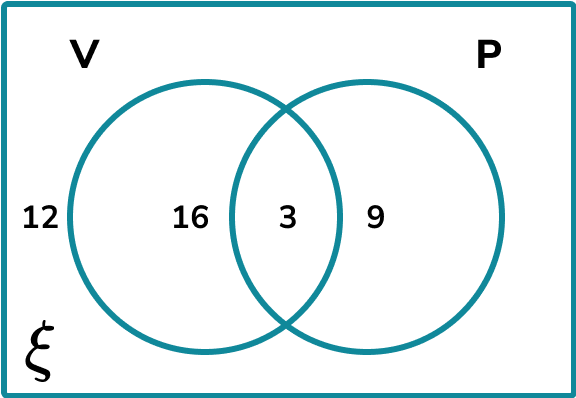
Calculate the probability of selecting a musician at random that can only play the violin.
Determine the parts of the Venn diagram that are in the subset.
The subset of musicians that can only play the violin is the set,
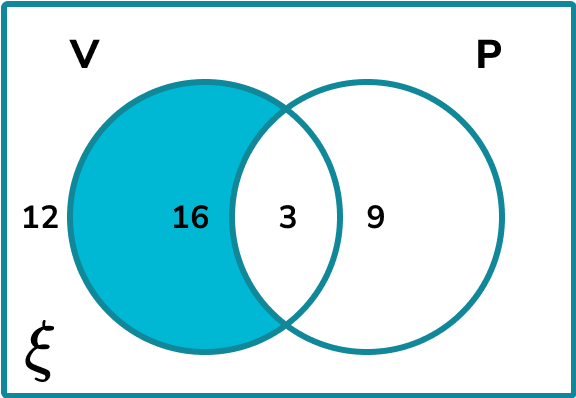
Calculate the frequency of the subset.
The frequency of musicians who can only play the violin is 16.
Calculate the total frequency of the larger set.
The larger set is every musician. We know that this total is 40 as it is given in the question (we can work this out by adding every frequency in the Venn diagram).
Write the probability as a fraction, and simplify.
The probability of picking a musician at random that can only play the violin is \frac=\frac.
70 students were asked about whether they have B= or C= for their break time snack. The results are shown in the Venn diagram below.
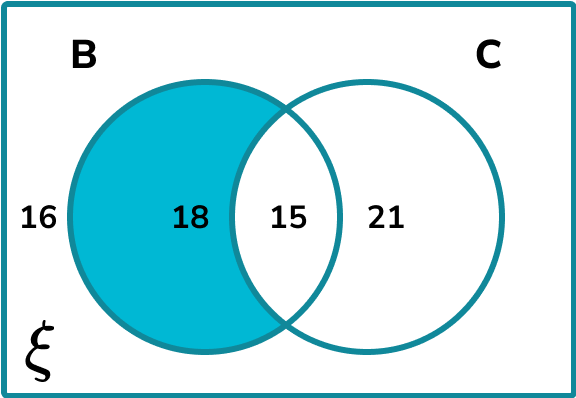
Calculate the probability of a student not having crisps given that they have biscuits.
Determine the parts of the Venn diagram that are in the subset.
We need to identify the subset which is the part of B that is not part of C,
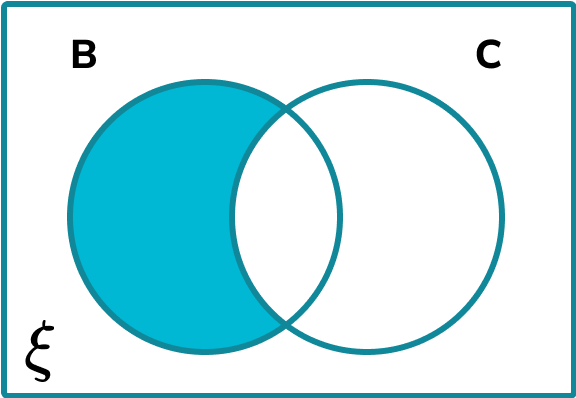
Calculate the frequency of the subset.
The frequency of values in the subset is 18.
Calculate the total frequency of the larger set.
In this case, we know the student has biscuits, so the population we are looking at is those in set B and we can ignore those not in set B.
The frequency of values in set B is 18+15 = 33.
Write the probability as a fraction and simplify.
The intersection is the overlap between two sets. If the item is only in Set A and not Set B, it must go in the subset that is just A, and not the intersection.
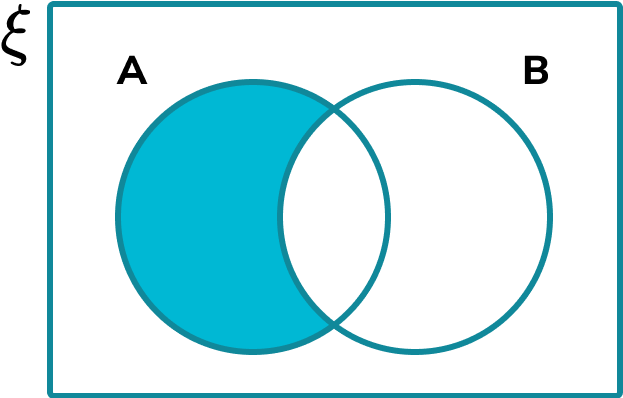
Make sure that every value within all of the sets is written into the Venn diagram. Count the items or add the frequencies to check your answer.
The universal set contains all of the items within every set given. If an item does not go in either circle, the item is written in the outer region, still within the rectangular universe.
It is possible that a set contains no items, or is the empty set. The frequency should therefore be written as 0, and not left blank.
Take for example the following two sets,
☐ Odd numbers less than 10
☐ Prime numbers less than 10
The Venn diagram is drawn so that the two sets are given as,
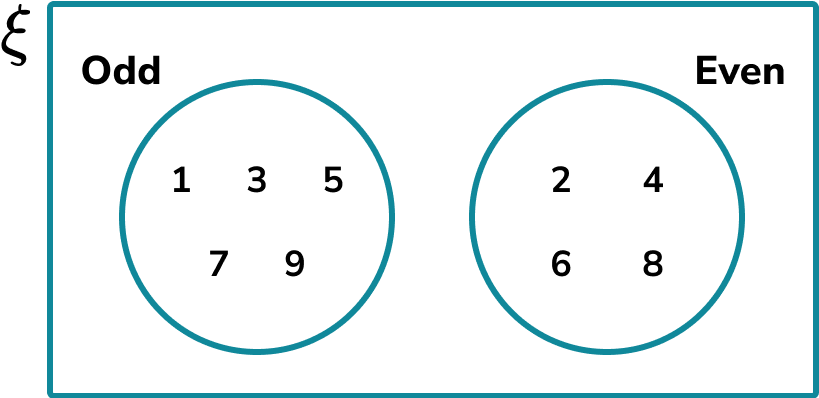
whereas the Venn diagram should look like this,
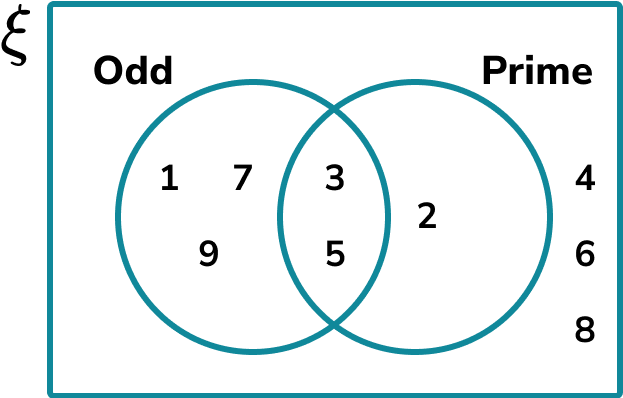
The set of A is written as A which consists of a list of items or a frequency.
The probability of A is written as P(A) and is a fraction. These two should not be confused.
For conditional probability, the denominator of the fraction will be a subset of the population, rather than the universal set.
The items that are placed in the intersection are sometimes incorrectly added twice, as it is assumed that the values are doubled as they belong to two sets. They only need to be counted once.
1. Let x be an integer. Construct a two set Venn diagram to represent the set \xi=\\> shared between the set of even numbers and the set of the multiples of 3.
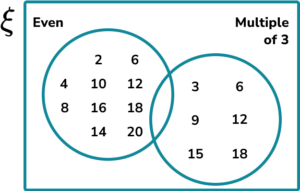

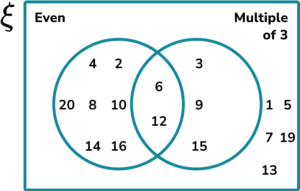

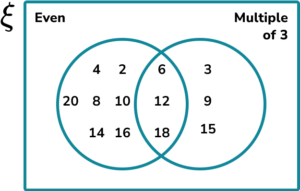

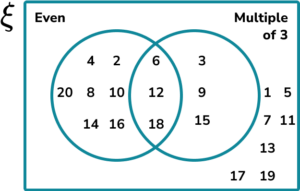

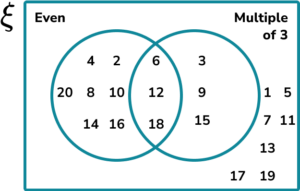
2. A group of people were asked about their phobias. Use the following information to complete the three set Venn diagram showing the results.
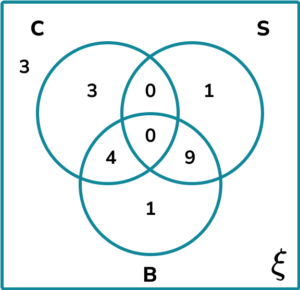

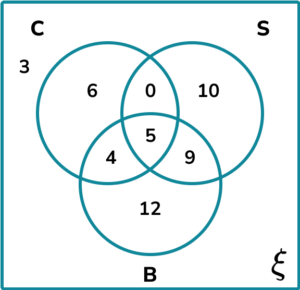

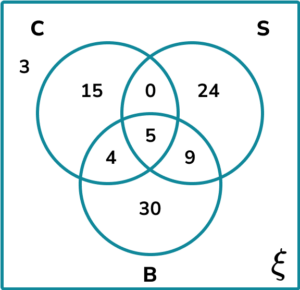

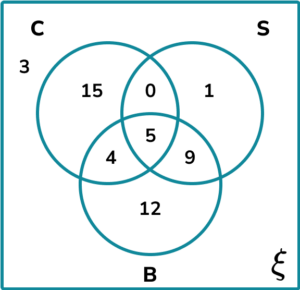

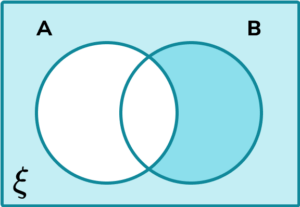
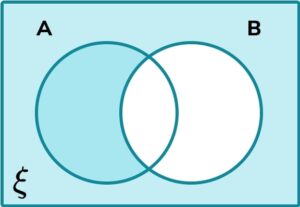
3. Determine the shaded region on the Venn diagram for the set \mathrm^ <\prime>\cap \mathrm^<\prime>.




4. A local pharmacy is carrying out some research. They would like to find out how many people have had one of the following three symptoms of flu:
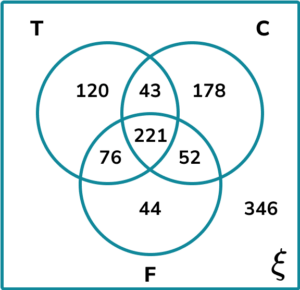
Calculate the frequency of people who had a cough or a fever, but not a temperature.




178 people had a cough only. 44 people had a fever only. 52 people had a cough and a fever, but not a temperature. The number of people that had a cough or a fever, but not a temperature is 178+52+44=274.
5. The Venn diagram below shows the names of 2D shapes that have at least one pair of parallel sides (P) or are quadrilateral (Q).
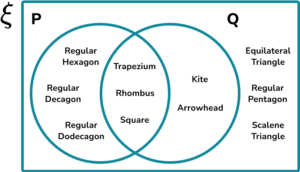
From the set \xi , determine P(P \cup Q)’.




The set (P \cup Q)’ contains all of the values that are not in the set P or Q,
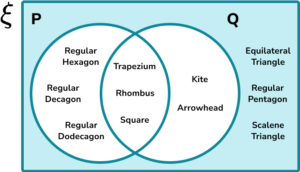
The three shapes that are in the shaded region are equilateral triangle, regular pentagon, and scalene triangle.
As there are 11 shapes in the Venn diagram,
6. A university’s entry requirements to study a degree in Medical Science is a grade A in Maths, and then a grade A in at least two of the three subjects: Chemistry, Biology, or Physics.
The Venn diagram below shows the frequencies of students who applied for the course and achieved an A grade in each subject.
Calculate P(C given that B \cup P).




The frequencies within each shaded region for the required subsets are,
‘
P(C given that B \cup P) = \frac.
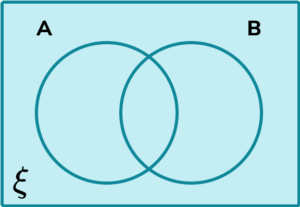
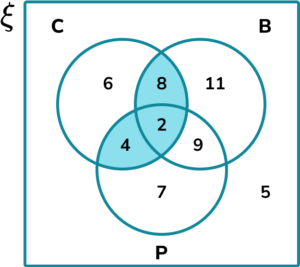
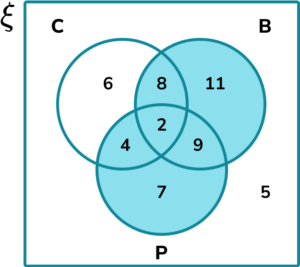
1. Shade the region in the Venn diagram that represents the set (A \cup B) \cap (A \cup C).
(1 mark)
Show answer
(1)
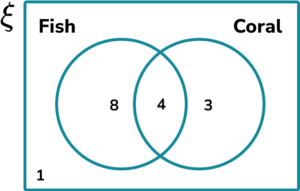
2. (a) A marine life park is opening a new underwater world consisting of 16 different tanks.
\frac of the tanks have coral and fish in them, \frac of the tanks contain fish only, and 1 tank does not contain fish or coral.
Draw a Venn diagram to show the distribution of Fish and Coral in the new underwater world tanks.
(b) How many tanks contain Coral?
(5 marks)
Show answer4 written in the intersection of Fish and Coral
(1)
8 written in Fish only
(1)
3 written in Coral only
(1)
1 written in the universal set
(1)
Solution:
(1)
3. (a) Members of a mountain rescue team were asking local walking groups whether they had any of the following emergency items: F = , B = , W = .
The results of their research were written into a Venn diagram:
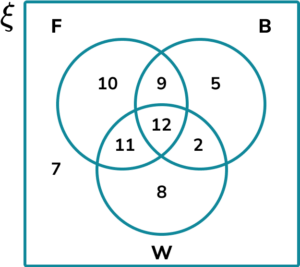
How many walking groups had at least 2 of the three emergency items with them?
(b) Calculate P(F \cap B \cap W). Give your answer as a simplified fraction.
(4 marks)
Show answer(1)
F \cap B \cap W =12
(1)
P(F \cap B \cap W) =\frac
(1)
(1)
You have now learned how to:
John Venn (1834-1923) was a mathematician, logician and philosopher who introduced the Venn diagram which we use widely in modern day statistics, probability, set theory and computer science. Clarence Irving wrote about the Venn diagram in his book ‘A survey of symbolic logic’ in 1918 after which Venn diagrams became more popular.
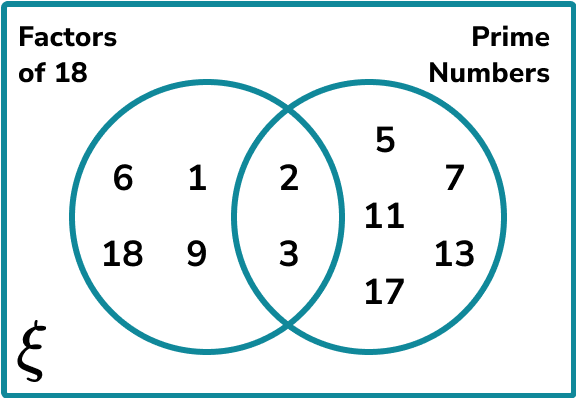
The Venn diagram below shows the relationship between the data set of Factors of 18, and the data set of Prime numbers less than 18.
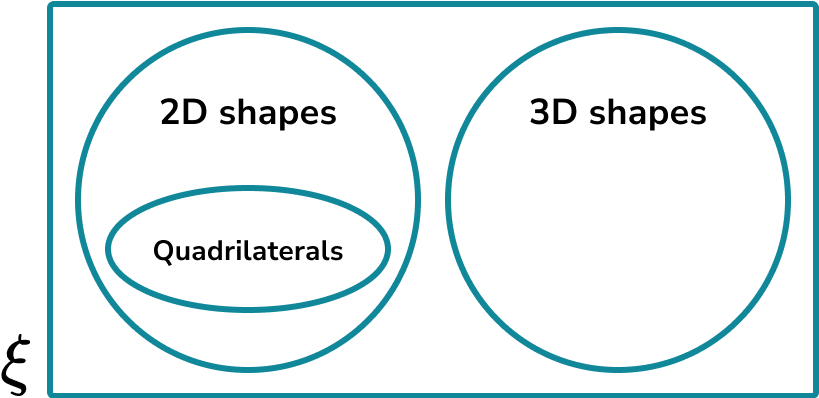
Leonhard Euler (1707-1783) was a pioneering Swiss mathematician who has greatly influenced today’s fundamental understanding of mathematics in areas such as fluid mechanics, complex analysis and calculus. An Euler diagram (sometimes referred to as Eulerian circles) is different to a Venn diagram because they only show relevant relationships, whereas a Venn diagram shows all possible relationships.
Take for example the set of 2D shapes and 3D shapes. These two sets cannot overlap as a 2D shape cannot be a 3D shape, however Quadrilaterals are a subset of 2D shapes and so they are contained entirely within the set of 2D shapes.
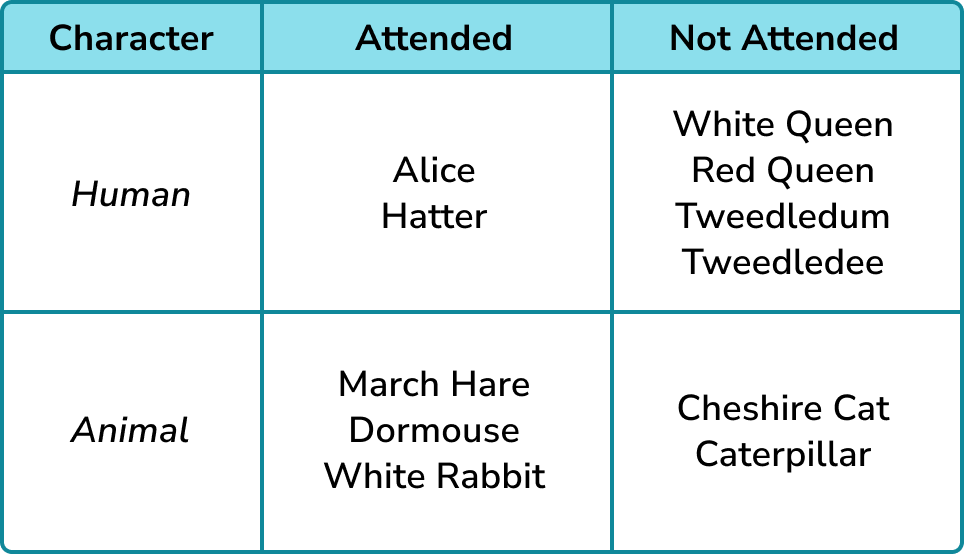
A Carroll diagram (named after the author and mathematician Lewis Carroll) is similar to a two-way table which categorises items within a set into smaller subsets.
For example, below is a Carroll diagram showing the Humans and Animals that did/not attend the tea party in the book ‘Alice in Wonderland’:
Note: A Venn diagram is named after John Venn and so ‘Venn’ should be capitalised (this is the same for Euler diagrams and Carroll diagrams as they are named after Leonhard Euler, and Lewis Carroll respectively).
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.